Smart Shots Overview
The Smart Shots Intervention
Interested in reading a reference cited on this page? They can be found
here:
Home / The Practice Problem / Literature References.
Project Aim
This project aims to demonstrate the feasibility and efficacy of evaluated vaccine forecasting clinical decision support in improving provider cognitive workload and task time in pediatric immunization management. The project is designed to be implemented without requiring the organization to commit to a long-term appraoach or incur the expense of an integrated solution. During the project pilot period, estimated from February through June 2025, evaluated vaccine forecast reports will be implemented for a group of volunteer provider participants to improve provider workflow and confidence in evaluating and managing pediatric immunization care. Information gathered and data generated from the project will help to inform future product roadmap and prioritization decisions.
This project has been evaluated and determined to be exempt from institutional review board oversight requirements under the federal regulations for the protection of human subjects ("The Common Rule"), 45 CFR 46, Subpart A, §46.104. Additonal information is available on the IRB information page.
Intervention: The Smart Shots Report
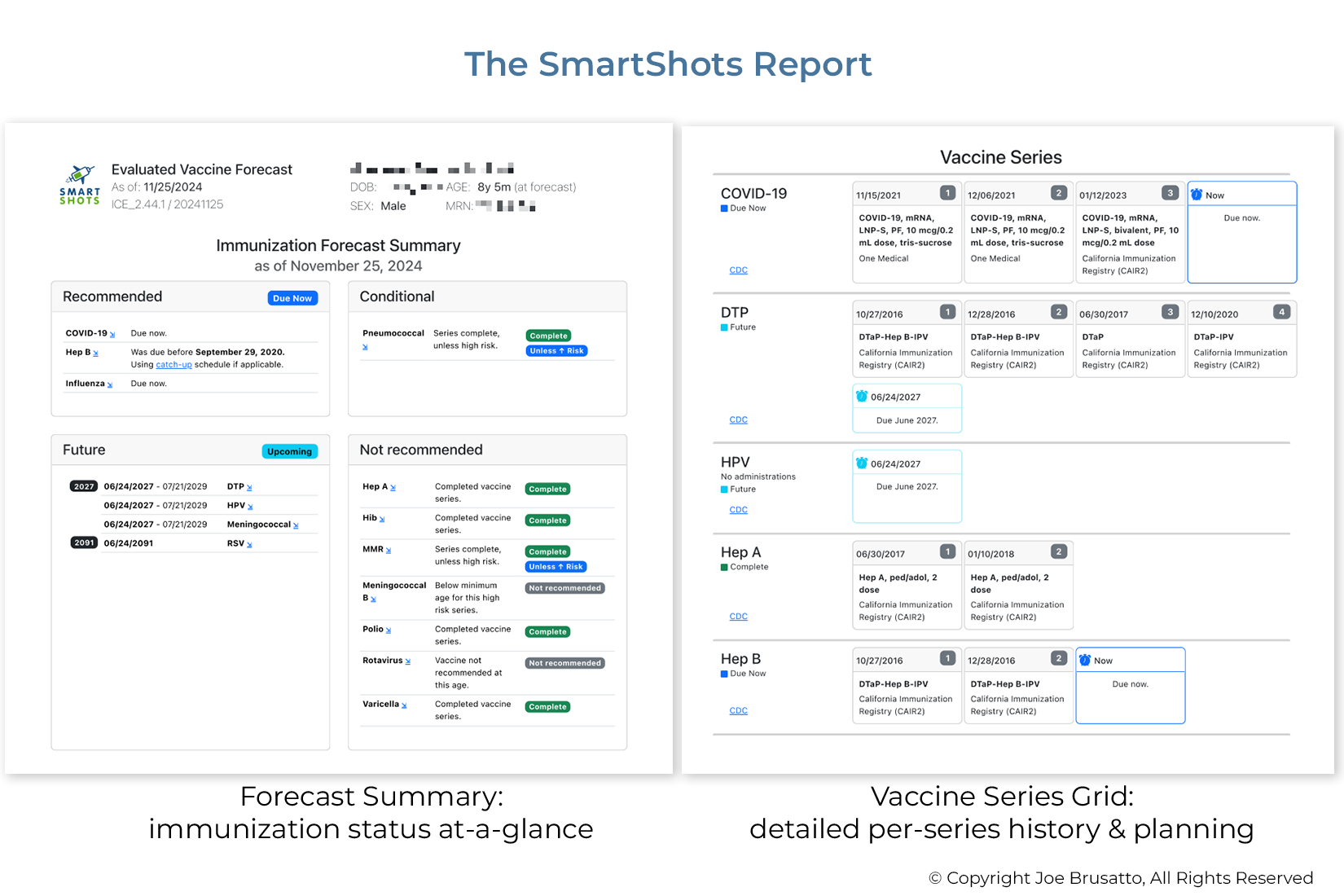
This project will utilize a report generated using an immunization-specific CDS solution, Immunization Calculation Engine (ICE). ICE uses input from patient demographics, EHR vaccine history, and current Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) clinical practice guidelines. In this project, the data output from ICE is then used to generate an easy-to-read report of the patient’s vaccination history and immunization needs which is uploaded to the patient chart in the EHR. The forecast includes vaccines currently due, those due in the future, and those conditionally recommended. The report also flags invalid historical doses and indicates if re-vaccination is required based on age and subsequent vaccination events.
Click here to learn more about the Smart Shots report and view sample reports.
Application of Cognitive Ergonomics
Cognitive ergonomics is a field of study within human factors and ergonomics that focuses on optimizing the interaction between individuals and systems by considering cognitive processes such as perception, memory, attention, and decision-making. It seeks to enhance the usability, efficiency, and safety of systems by designing interfaces, tools, and workflows that align with human mental capabilities and limitations. This discipline is particularly relevant in high-stakes environments like aviation and healthcare where cognitive load and decision-making accuracy are critical.
By applying principles of cognitive ergonomics, designers can minimize errors, reduce mental strain, and improve overall system performance, ensuring that technologies complement rather than hinder human cognition thereby addressing contributors to cognitive load, performance, errors, and burnout (Branaghan & Lafko, 2020; Kroth et al., 2019; Mazur et al., 2019). The report used in the intervention was developed using cognitive ergonomics principles and the design is optimized for cognitive workload factors of attention, working memory, and decision-making (Branaghan & Lafko, 2020; Li-Wang et al., 2023).
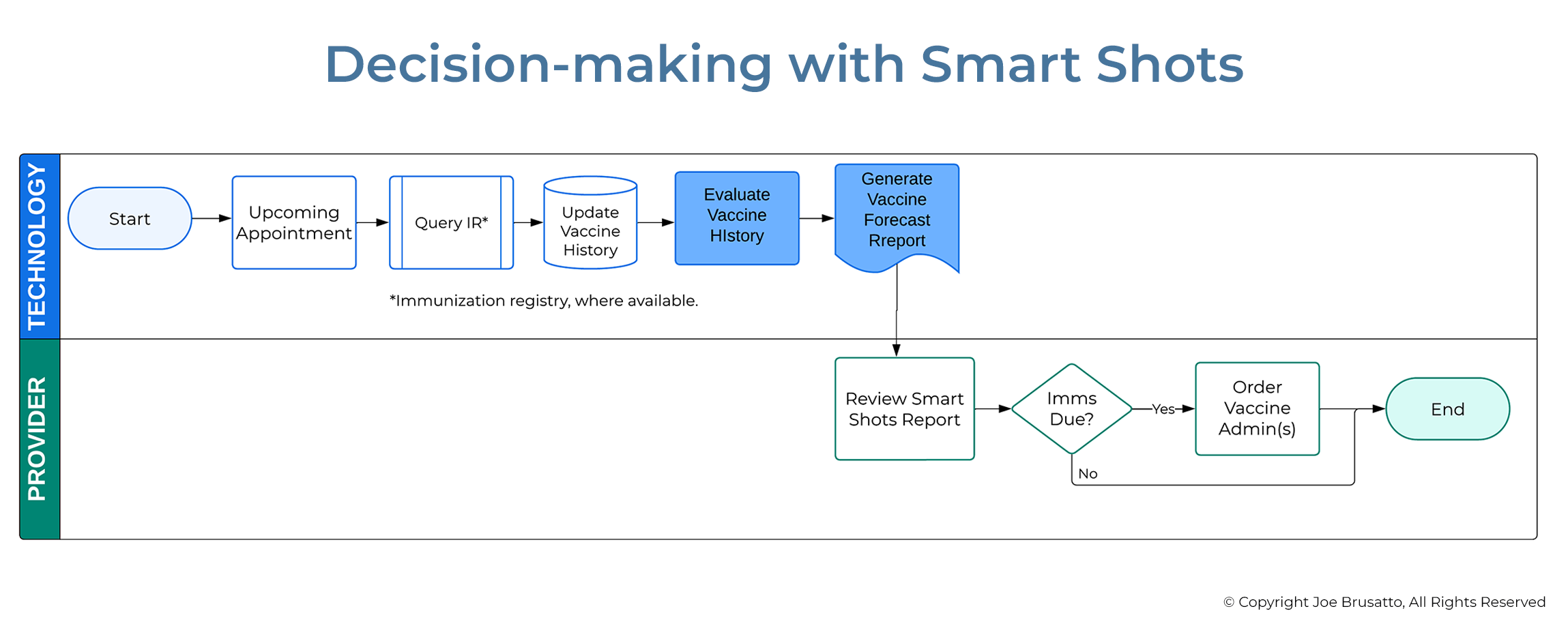
Impact on The Decision-making Process
The CDS process and Smart Shots report offload the routine, automatable portions of the decision-making process to technology. This greatly simplifies the providers' cognitive work and frees working memory for other tasks that require human cognition.
To see how this process looks without Smart Shots, see the process diagram in The Practice Problem.
Provider Participation
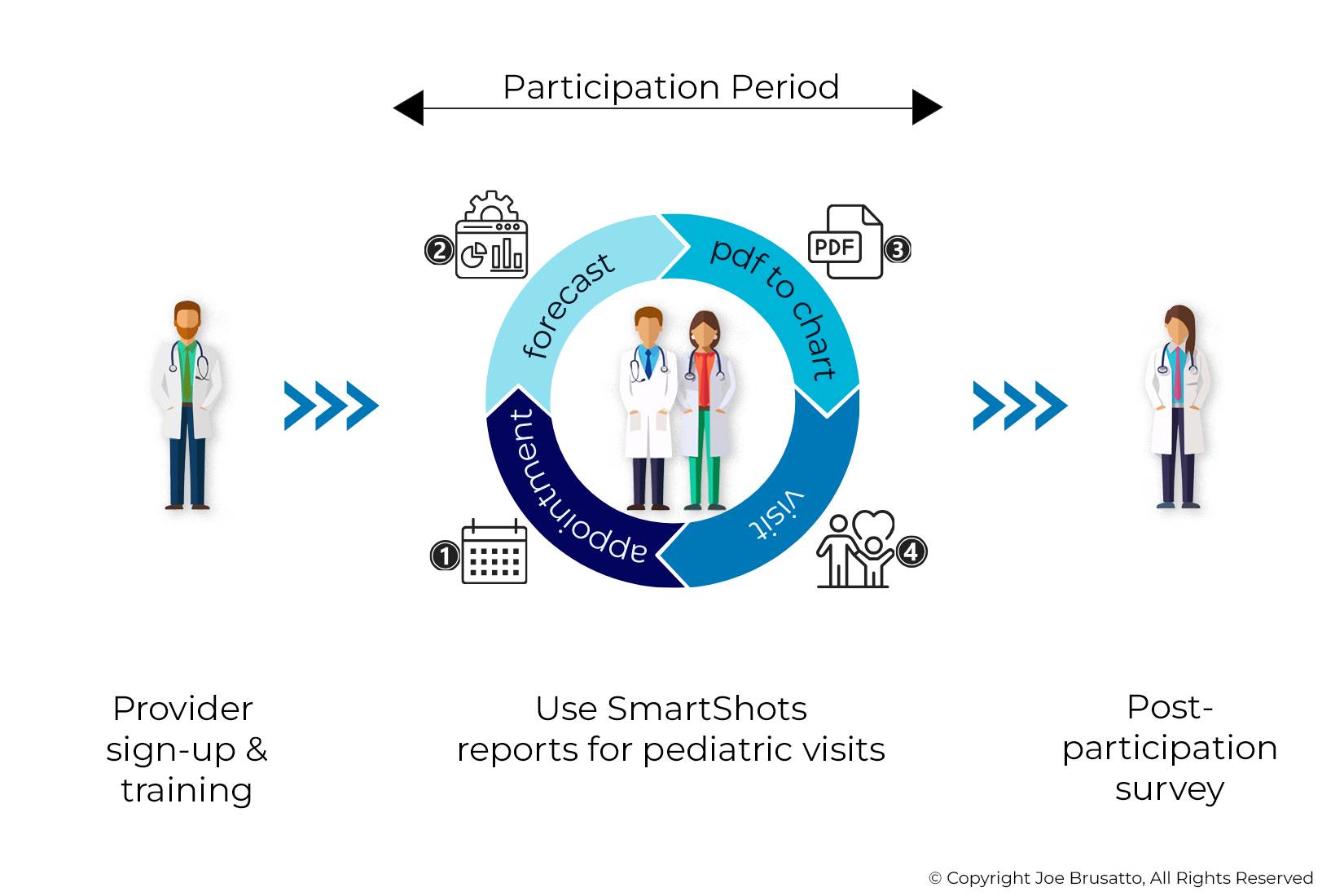
Practice setting providers who deliver immunization-related care during in-person visits for patients under 19, regardless of pediatric panel size or profession, are eligible to participate in the project. Providers will be recruited through an email campaign; participation is voluntary, and participants may end their involvement at any time. No pre-defined limit on the number of participants has been set, and all those interested are expected to be accommodated. The duration and timeframe for participation will be determined based on the results of recruitment efforts. It is anticipated that if there is a large number of participants, participation will be staggered, and durations may be shortened, but in no case to less than four weeks. At the end of their participation, providers will complete a post-participation survey and revert to their previous workflow.
Providers interested in participating in the project can sign up here.
The collection of personally identifiable provider information will be limited to that necessary for administration of the project. Participant survey data will be collected anonymously. Additonal information is available on the IRB information page.
Report Generation
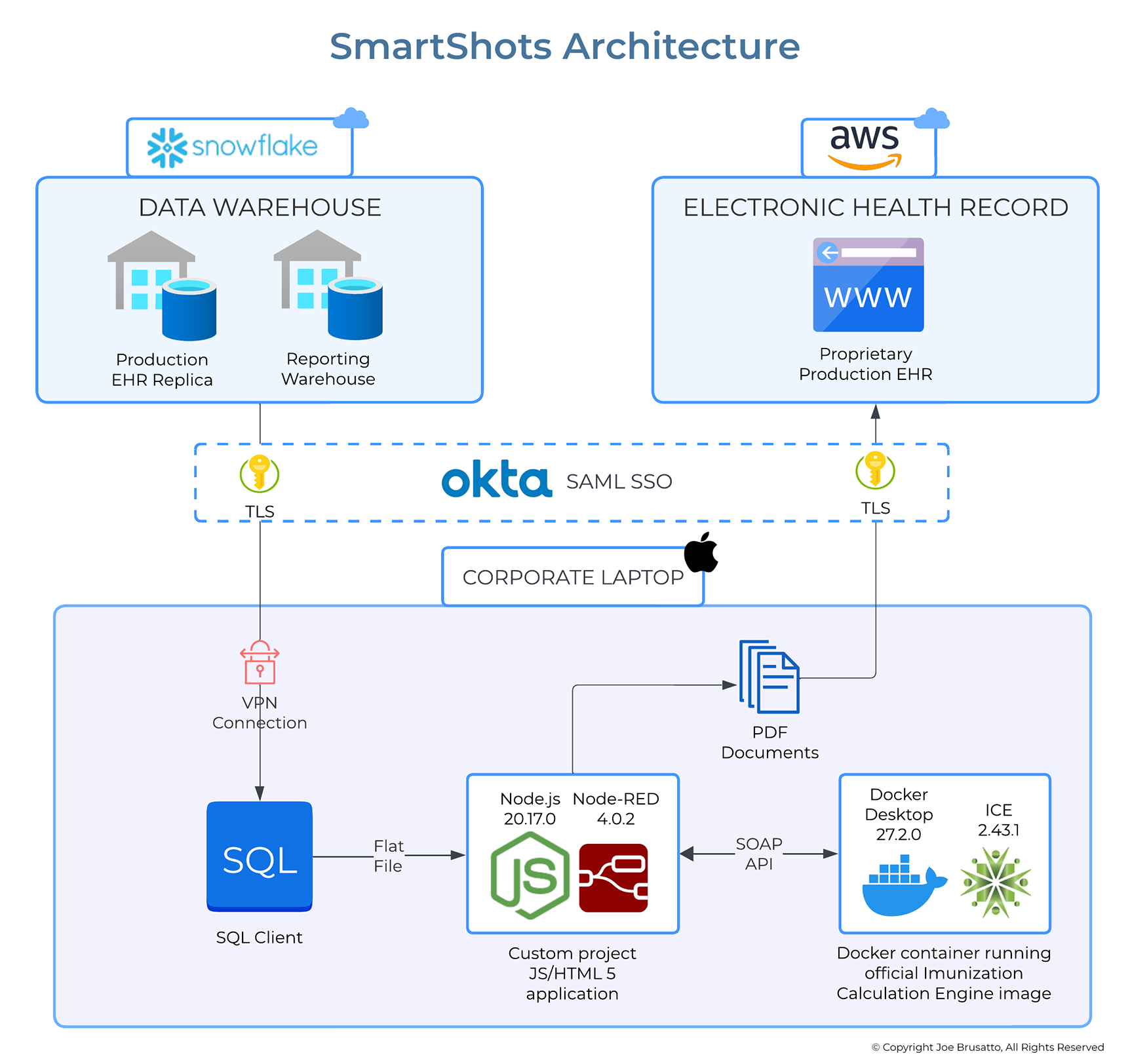
Each morning, immunization history for the participant’s pediatric patients with scheduled appointments for that day is exported to a flat file on a corporate laptop. This timing ensures that updates from immunization registries, which occur 24 hours before appointment time, are applied to patient charts and available in the data warehouse before the export. The Smart Shots application imports the flat file and generates an HL7 Virtual Medical Record (vMR) representation of the patient’s immunization history. The application then calls a SOAP API on an Immunization Calculation Engine (ICE) service running in a local Docker instance, which evaluates the data and returns a vMR response. The response data for each patient is processed and saved as a JSON file on the local machine, which is used to render and save the Smart Shots report as a PDF file. The file is manually uploaded to the patient’s chart using an EHR utility. After processing each day, all PHI, including the source data file, JSON file, and PDF, are deleted from the local machine.
About Immunization Calculation Engine
ICE was developed in partnership with the New York City Department of Health and has been used for nearly a decade in the New York Citywide Immunization Registry (CIR). Since its release, the developers have made ICE freely available for use or modification at no cost (Arzt et al., 2022). This type of algorithmic vaccine forecasting has demonstrated efficacy in improving vaccination rates and gap closures (Bacci et al., 2019; Rand & Humiston, 2021; Stephens et al., 2021) and has been recommended as a standard of care in immunization management (Hunter et al., 2020). While ICE is designed to be integrated into systems such as EHRs and IRs, engineering resource constraints make this level of integration infeasible for the practice site at this time.
This project employs a novel use of the ICE engine to produce vaccine forecast reports, which are uploaded to the EHR chart.
Improvement Framework
Smartshots has been designed using the (PDSA) framework, a cyclical, iterative model for quality improvement that enables systematic testing and refinement of changes in real-world settings. It consists of four stages:
- Plan, where objectives are defined, changes are designed, and success measures are established;
- Do, where the planned intervention is implemented on a small scale;
- Study, where data is analyzed to assess the impact of the change; and
- Act, where successful changes are adopted, modified, or expanded, while unsuccessful ones are adjusted or abandoned.
This structured approach of PDSA helps organizations continuously improve processes, reduce errors, and enhance efficiency through evidence-based decision-making.
